Persistant Dry, Itchy Skin
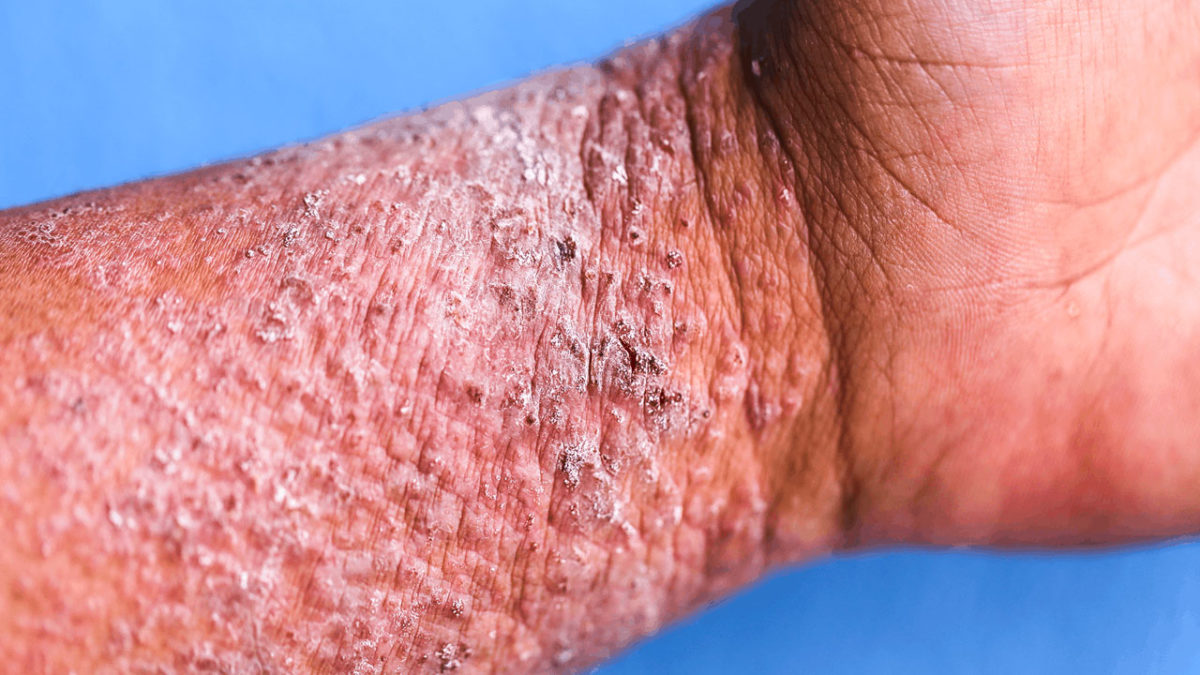
Eczema is not just a childhood disease. Adults can get any type of eczema, including atopic dermatitis (AD), even though many people consider eczema only a childhood disease. Eczema can occur at any stage of life. A peak time for developing adult-onset AD is in your 50s.
For some children, the AD never goes away, so it’s a lifelong disease. This happened to Peter Moffat, the award-winning writer of the British TV series Criminal Justice. You can read about how AD affects his life by going to: Adults with eczema too often suffer in silence.
Even if you had AD as a child, your skin can look and feel differently when you have AD as an adult. That’s actually one of the most striking differences between AD in adults and AD in children.
In adults, the skin tends to be extremely dry and scaly where the AD appears. If you’ve had AD for years, patches of your skin may be thick, leathery, and darker (or lighter) than the surrounding skin. Years of scratching causes this. The thickened skin can itch all the time. Adults also tend to get AD on different parts of their bodies than do children. When an adult has AD, it’s most likely to form in one or more of these areas:
- Backs of the knees
- Crooks of the elbows
- Back of the neck
- Face
Adults, unlike children, often have AD around their eyes. You’ll often see thickened, darker skin circling the eyes, as shown in the picture on this page. The skin around the eyes also tends to be very itchy.
AD shows up with many of the following symptoms in both adults and children:
- Appear anywhere on the skin
- Be intensely itchy
- Cause sleep loss due to the itch
- Make you feel depressed, anxious, or both
- Lead to skin infections
- Increase your risk of developing asthma, hay fever, and other allergies
- Decrease your quality of life if left untreated
The numbers are showing that more children and adults are developing AD than ever before. Dermatologists are not sure why this increase in AD cases is happening. What they have discovered is that AD can worsen without treatment. While AD causes some obvious signs and symptoms, other types of eczema can cause intensely itchy patches of skin. These include:
- Nummular eczema
- Neurodermatitis
- Hand eczema
- Dyshidrotic eczema
- Pityriasis alba
Each of these skin conditions requires different treatment, so it’s important to know which one you have. By seeing a board-certified dermatologist, you’ll get the expertise you need for an accurate diagnosis. A dermatologist can also create a treatment plan tailored to your individual needs. And that can bring welcomed relief.
Dr. Moore treats atopic dermatitis and may have a clinical trial with free medicine and treatment. Please ask about this on your next visit in our office.
(Source AAD.org)







