CLASSIC LIST
This time of year we are reminded of the gifts of Gold, Frankincense, and Myrrh – gifts fit for a king! There are actually medically beneficial properties to both Frankincense and Myrrh.
The Boswellia serrata exudate or gum (known in India as “guggulu”) that forms an aromatic resin traditionally used as incense – and known as frankincense (especially when retrieved from Boswellia species found in Eritrea and Somalia but also from the Indian variety) – has been considered for thousands of years to possess therapeutic properties. It is used in Ayurvedic medicine, as well as in traditional medicine in China and the Middle East, particularly for its anti-inflammatory effects to treat chronic conditions. In fact, such essential oils have been used since 2800 BC to treat various inflammatory conditions, including skin sores and wounds, as well as in perfumes and incense. In the West, use of frankincense dates back to thousands of years as well, more often found in the form of incense for religious and cultural ceremonies.Over the past 2 decades, evidence supporting the use of frankincense for therapeutic medical purposes has increased, particularly because of its purported anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties.
Terpenoids and essential oils are the primary components of frankincense and are known to impart anti-inflammatory and anticancer activity. The same is true for myrrh, which has been combined with frankincense in traditional Chinese medicine as a single medication for millennia, with the two acting synergistically and considered still to be a potent combination in conferring various biological benefits.
In 2010, in a systematic review of the anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities of Boswellia species and their chemical ingredients, Efferth and Oesch found that frankincense blocks the production of leukotrienes, cyclooxygenase (COX) 1 and 2, as well as 5-lipoxygenase; and oxidative stress. It also contributes to regulation of immune cells from the innate and acquired immune systems and exerts anticancer activity by influencing signaling transduction responsible for cell cycle arrest, as well as inhibition of proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. The investigators also reported on clinical trial results that have found efficacy of frankincense and its constituents in ameliorating symptoms of psoriasis and erythematous eczema, among other disorders.
Another study completed in 2016 sought to identify the active ingredients responsible for the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of frankincense. They found that alpha-pinene, linalool, and 1-octanol were key contributors. These constituents were noted for suppressing COX-2 overexpression in mice, as well as nociceptive stimulus-induced inflammatory infiltrates.
A 2017 study evaluated the biological activities of the essential oil in pre-inflamed human dermal fibroblasts using 17 key protein biomarkers. Frankincense essential oil displayed significant antiproliferative activity and suppressed collagen III, interferon gamma-induced protein 10, and intracellular adhesion molecule 1. The investigators referred to the overall encouraging potential of frankincense essential oil to exert influence over inflammation and tissue remodeling in human skin and called for additional research into its mechanisms of action and active constituents.
The main active ingredient in frankincense, boswellic acid, has been shown to promote apoptosis, suppress matrix metalloproteinase secretion, and hinder migration in metastatic melanoma cell lines in mice. A 2019 study. demonstrated that frankincense essential oil yielded substantial antimelanoma activity in vitro and in vivo and ameliorated hepatotoxicity caused by acetaminophen.
The use of frankincense in traditional medicine has a long and impressive track record. Recent research provides reason for optimism, and further investigating the possible incorporation of this botanical agent into modern dermatologic therapies appears warranted. Clearly, however, much more research is needed.
Summer temperatures and summer activities require good care of your skin. Proper and frequent use of broad spectrum sunscreens is essential for protection for your skin from harmful UV rays and from burns and potential sunburn pain. While using sunscreens you should be aware that a number of Neutrogena and Aveeno products have been voluntarily recalled by their manufacturer. These companies recently pulled several sunscreens from market shelves after independent testing had found they were contaminated with a cancer-causing chemical called benzene. The National Cancer Institute has stated that exposure to benzene increases the risk of developing leukemia and other blood disorders. CVS Health also stopped selling two of its after-sun care products due to similar findings.
The vast majority of tested sunscreens, however, were free of benzene, and experts stress the importance of sunscreen use to protect skin from the aging and cancerous effects of the sun.
All batches, or lots, of these four Neutrogena spray sunscreens and one Aveeno spray were voluntarily recalled this week by parent company Johnson & Johnson (J&J) “out of an abundance of caution”:
Neutrogena® Beach Defense® aerosol
Neutrogena® Cool Dry Sport aerosol
Neutrogena® Invisible Daily™ defense aerosol
Neutrogena® Ultra Sheer® aerosol
Aveeno® Protect + Refresh aerosol
Benzene is not an ingredient in any of these sunscreen products, but it was detected in some samples of the impacted aerosol sunscreen finished products. The manufacturer of these products is recommending that consumers should stop using these specific products and appropriately discard them.
Specific lots of all recalled Neutrogena and Aveeno sunscreens can be found here , and customers can call with questions and request a refund by completing this form, or calling 1-800-458-1673.
CVS also stopped selling CVS Health After Sun Aloe Vera and CVS Health After Sun Aloe Vera Spray a day after the Johnson & Johnson recall was announced. CVS Health’s corporate communications, told CNN the company is “cooperating with Johnson & Johnson’s voluntary recall.”
“CVS products have not been recalled,” but the company has paused sales of the two CVS products, which tested positive for benzene, “out of an abundance of caution.” CVS Health is working with the supplier of the products to “take appropriate additional steps.”
Why were the sunscreens recalled?
The voluntary recalls and pause in sales came after an independent lab tested 294 samples from 69 brands of sprays, lotions, gels and creams designed to protect the skin from the sun or care for the skin after sun. Of those, 78 samples tested positive for benzene.
Contamination appeared in specific batches of sunscreen, rather than a specific brand, said David Light, CEO and founder of Valisure, the independent lab that ran the tests. “The finding of benzene in sunscreen was certainly surprising to me as a scientist and a consumer. I’m quite a heavy user of sunscreen myself; I have five kids and we all use sunscreen, so it was rather concerning to find such high levels,” Light said.
Multiple samples contained “significantly detectable benzene and some batches contained up to 3.1 times the conditionally restricted limit,” according to the citizen petition asking for action that Valisure filed with the US Food and Drug Administration. “We petitioned the FDA to recall or to request recalls of the products that are 0.1 per million and above,” Light told CNN. “It’s obvious that we shouldn’t be taking that risk, and we just wanted it cleaned up.”
Samples of three of the recalled Neutrogena spray sunscreens — Beach Defense, Invisible Daily and Ultra Sheer — and one CVS brand — After-sun Aloe Vera Soothing Spray — had levels of benzene that were 2 parts per million or higher, according to Valisure’s tests. Another spray, Neutrogena’s Cool Dry Sport, and CVS Health’s After-sun Aloe Vera Moisturizing Gel, tested at .01 to 2 parts per million of benzene in some samples. Aveeno’s Protect + Refresh aerosol, which was the fifth sunscreen recalled by J&J, was not tested by Valisure.
Samples of three Banana Boat products also contained levels of benzene at those levels: Kids Max Protect & Play Sunscreen C-Spray SPF 100, UltraMist Deep Tanning Dry Oil Continuous Clear Spray SPF 4 and Ultra Sport Clear Sunscreen Spray SPF 100.
The sunscreens tested by Valisure were only a tiny sample of the more than 11,000 registered sun care products on the market. The Personal Care Products Council, an industry association, said its members were “firmly committed” to providing products with “ingredients that have been thoroughly tested for safety and follow the requirements of the law.” “We are aware of the study reporting the presence of benzene in some of the sunscreen products tested,” the council said in a statement. “There is nothing more important than safety. If our consumers can’t believe in a product or rely on it to do what it says, then nothing else matters.”
What is benzene?
Benzene is a natural component of crude oil, gasoline and cigarette smoke and ranks in the top 20 chemicals used for production of “lubricants, rubbers, dyes, detergents, drugs, and pesticides,” as well as “plastics, resins, and nylon and synthetic fibers,” according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
At room temperature, benzene is a colorless or light yellow liquid with a sweet odor. Highly flammable, it will float on water, and while it evaporates quickly, it is heavier than air and can sink into low-lying areas, the CDC noted.
Gas emissions from volcanoes and forest fires are natural sources of benzene, but the largest sources are emissions from burning coal and oil, motor vehicle exhaust, and evaporation from gasoline service stations, according to the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR).
Exposure to high levels of benzene in the air can cause death, the ATSDR says, but the impacts of eating foods or drinking liquids containing lower levels of benzene are not known. “If you spill benzene on your skin, it may cause redness and sores. Benzene in your eyes may cause general irritation and damage to your cornea,” the ATSDR said.
Cigarette smoke and off-gassing from furniture wax, detergents, glue and paint are sources of indoor exposure to benzene, according to the CDC, while outdoor air can be polluted with benzene from “gas stations, motor vehicle exhaust, and industrial emissions.”
How did benzene get into sunscreens?
No one knows for sure how the toxin ended up in sun care products. Benzene was not an ingredient in any of the sunscreens, so experts suspect contamination had to have occurred during the manufacturing process.
“There are a lot of theories,” said Scott Faber, the senior vice president of government affairs for the Environmental Working Group (EWG), a non-profit consumer health advocacy group which puts out a yearly guide to safe sunscreens.
“Benzene could be a byproduct of the process of making the chemicals that companies sell to the formulators of personal care products and sunscreens. Or it could be that some of those chemicals break down into benzene, although that seems less likely,” Faber said.
“But it’s very alarming, especially since the FDA does not require companies to test ingredients for contaminants, nor does it require testing for such chemicals at a finished product stage,” he added.
What is the FDA doing?
In response to Valisure’s petition, the FDA told CNN that it “evaluates and assesses the information provided in citizen petitions of this type and, generally, initiates an independent testing and verification process.”
“While the FDA evaluates the citizen petition submitted by Valisure, we will continue to monitor sunscreen manufacturing and marketing to help ensure the availability of safe sunscreens for U.S. consumers,” an FDA spokesperson said.
Benzene is not the only concern when it comes to sunscreen. A number of sunscreens have been shown to be ineffective or contain chemicals that can enter the bloodstream and disrupt hormones. In EWG’s 2021 guide to sunscreens, they analyzed over 1,800 products and found that 75% did not provide adequate sun protection — or included ingredients linked to harm. Still, there were over 200 products that did meet their safety standards.
All of this uncertainty may leave consumers unsure of what to do, and experts worry some may forgo the use of sunscreen altogether. But, experts warned, that’s an even worse idea. Melanoma, one of the most deadly forms of skin cancer, has been on the rise globally for decades. And while survival rates are getting better, melanoma is still the fifth most commonly diagnosed cancer in the United States.
And of course, it’s always a great choice to use common sense practices as well to protect your skin from harmful rays. Wear shorts, shirts, pants and hats to help block dangerous rays and apply safe sunscreens to exposed skin. Wisely choose your time in the sun by avoiding the most intense rays between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. and seek shade whenever possible.
Dr. Angela Moore and Arlington Center for Dermatology offer a number of safe, Benzene-FREE, sunscreens that are just right for you and your family. Ask your provider about which sunscreen would be best for you.
Source: CNN July 17, 2021 Sandee LaMotte
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a little-known disease that causes deep and painful lumps under the skin, usually in the armpits or groin.
Many people mistake the deep lumps for painful pimples or acne cysts. HS can also be misdiagnosed as boils, infected hair follicles (folliculitis), or a sexually transmitted disease.
Because HS is often mistaken for another condition, people can go years without getting the care they need. Some people live with HS for 12 years or longer before getting diagnosed.
Without the right diagnosis and individualized treatment, HS can worsen. What starts out as one or two deep, painful, pimple-like lumps can turn into several lumps. In time, these lumps can break open and leak a foul-smelling liquid. The lumps can continue to return, rupture, and heal.
Patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have a high prevalence of acne vulgaris, research published in Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology shows. Furthermore, the mean age of onset of hidradenitis suppurativa patients is lower when they also have acne vulgaris, the data show.
The prevalence of acne vulgaris was assessed in consecutive new patients with hidradenitis suppurativa referred to the Department of Dermatology at Bispebjerg Hospital in Copenhagen, Denmark.
A total of 302 patients (191 women and 111 men) with a mean age of 39.4 years referred between January 1, 2016 and October 8, 2018 were included in the evaluation.
The overall prevalence of acne vulgaris was 21.2%. Nineteen of the patients with acne vulgaris (29.7%) had hidradenitis suppurativa assessed as Hurley stage I, 39 (60.9%) Hurley stage II and 6 (9.4%) Hurley III. There was no statistical difference in Hurley stage of hidradenitis suppurativa between patients with and without acne.
However, acne vulgaris was associated with a lower age of onset of hidradenitis suppurativa. Those patients with hidradenitis suppurativa and acne vulgaris attending the clinic were significantly younger than those without acne vulgaris (33.8 versus 40.8 years,), and the mean age at onset of hidradenitis suppurativa was significantly lower in patients with acne vulgaris than it was in those without (21.4 versus 27.2 years).
Hidradenitis suppurativa patients with acne vulgaris also had lower levels of plasma inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein [CRP], neutrophils, and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio [NLR]) than those without acne vulgaris.
Prevalence of acne vulgaris among hidradenitis suppurativa patients was not impacted by the sex of the patient, smoking status, obesity or diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). There was also no difference in Dermatology Quality of Life Index (DLQI) and localization of hidradenitis suppurativa between the patients with and without acne vulgaris.
Patients referred for specialized hospital care tended to have a high prevalence of acne vulgaris. Furthermore, hidradenitis suppurativa patients with acne vulgaris tend to have a significantly lower mean age and age at onset of hidradenitis suppurativa compared to hidradenitis suppurativa patients without acne vulgaris. These findings call for greater awareness of this association between acne and HS and for a co-management approach to treatment.
The Danish findings support those of a population-based sample from the United states which found that the prevalence of acne vulgaris was 15.2% among adults with hidradenitis suppurativa, compared to 2.9% in adults without hidradenitis suppurativa.
The US cross-sectional analysis used electronic health records data from a population-based sample of over 55 million patients to identifying adults with acne vulgaris among patients with and without hidradenitis suppurativa.
Prevalence of acne vulgaris in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa was found to be 15.2% (7,315 /48,050), compared to 2.9% (497,360 /16,899,470) for adults without hidradenitis suppurativa. Prevalence of acne vulgaris was greatest among hidradenitis suppurativa patients who were female (16.4%), aged 18-44 years (18.2%), non-white (17.5%), obese (15.5%), and had PCOS (28.7%).
Hidradenitis suppurativa patients had 4.51 times the odds of having acne vulgaris compared to non-HS patients, and the association between hidradenitis suppurativa and acne vulgaris was generally stronger for patients who were male, aged ≥ 65 years, non-whites, and obese.
The association between acne vulgaris and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is already well established. Recent research has demonstrated that approximately 1 in 11 women with hidradenitis suppurativa also have PCOS. The link among the three conditions is not yet clearly established, as circulating and end organ androgen expression appear to be normal among hidradenitis suppurativa patients.
If you have signs of HS or acne, have your dermatologist examine for both as HS may not be easily recognized by the general public. Dr. Moore’s research team, Arlington Research Center, his screening patients for HS to participate in clinical trials for HS. We also have clinical trials for acne. Contact Arlington Research Center at studies@acderm.com or 817-795-7546 ext. 339 to see if you qualify for an HS clinical trial.
Sources: AAD.org and Dermatology News February 2019
- Between 30 and 50 years of age
- Fair-skinned, and often have blonde hair and blue eyes
- From Celtic or Scandinavian ancestry
- Likely to have someone in their family tree with rosacea or severe acne
- Likely to have had lots of acne — or acne cysts and/or nodules
- Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea – Redness, flushing, visible blood vessels
- Papulopustular rosacea – Redness, swelling, and acne-like breakouts
- Phymatous rosacea – Skin thickens and has a bumpy texture
- Ocular rosacea – Eyes red and irritated, eyelids can be swollen, and the person may have what looks like a sty.
FDA is alerting consumers of Saniderm Products and UVT Inc.’s voluntary recall of Saniderm Advanced Hand Sanitizer. Following FDA’s recommendation, two distributors – Saniderm Products and UVT – agreed to recall Saniderm Advanced Hand Sanitizer packaged in 1-liter plastic bottles and labeled with “Made in Mexico” and “Produced by: Eskbiochem SA de CV.”
The UVT hand sanitizer is labeled with lot number 0530 and an expiration date of 04/2022. The Saniderm Products hand sanitizer is labeled with lot number 53131626 and “Manufactured on April/1/20.”
FDA advises consumers not to use any hand sanitizer manufactured by Eskbiochem SA de CV in Mexico, due to the potential presence of methanol (wood alcohol), a substance that can be toxic when absorbed through the skin or ingested. FDA has identified the following products manufactured by Eskbiochem:
- All-Clean Hand Sanitizer (NDC: 74589-002-01) Esk Biochem Hand Sanitizer (NDC: 74589-007-01)
- CleanCare NoGerm Advanced Hand Sanitizer 75% Alcohol (NDC: 74589-008-04)
- Lavar 70 Gel Hand Sanitizer (NDC: 74589-006-01)
- The Good Gel Antibacterial Gel Hand Sanitizer (NDC: 74589-010-10)
- CleanCare NoGerm Advanced Hand Sanitizer 80% Alcohol (NDC: 74589-005-03)
- CleanCare NoGerm Advanced Hand Sanitizer 75% Alcohol (NDC: 74589-009-01)
- CleanCare NoGerm Advanced Hand Sanitizer 80% Alcohol (NDC: 74589-003-01)
- Saniderm Advanced Hand Sanitizer (NDC: 74589-001-01)
FDA tested samples of Lavar Gel and CleanCare No Germ. Lavar Gel contains 81 percent (v/v) methanol and no ethyl alcohol, and CleanCare No Germ contains 28 percent (v/v) methanol. Methanol is not an acceptable ingredient for hand sanitizers and should not be used due to its toxic effects.
Consumers who have been exposed to hand sanitizer containing methanol should seek immediate treatment, which is critical for potential reversal of toxic effects of methanol poisoning. Substantial methanol exposure can result in nausea, vomiting, headache, blurred vision, permanent blindness, seizures, coma, permanent damage to the nervous system or death. Although all persons using these products on their hands are at risk, young children who accidently ingest these products and adolescents and adults who drink these products as an alcohol (ethanol) substitute, are most at risk for methanol poisoning.
On June 17, 2020, FDA contacted Eskbiochem to recommend the company remove its hand sanitizer products from the market due to the risks associated with methanol poisoning. To date, the company has not taken action to remove these potentially dangerous products from the market. Therefore, FDA recommends consumers stop using these hand sanitizers and dispose of them immediately in appropriate hazardous waste containers. Do not flush or pour these products down the drain.
FDA reminds consumers to wash their hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after going to the bathroom; before eating; and after coughing, sneezing, or blowing one’s nose. If soap and water are not readily available, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend consumers use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer that contains at least 60 percent ethanol.
FDA remains vigilant and will continue to take action when quality issues arise with hand sanitizers. Additionally, the agency is concerned with false and misleading claims for hand sanitizers, for example that they can provide prolonged protection such as 24-hours against viruses including COVID-19, since there is no evidence to support these claims.
To date, FDA is not aware of any reports of adverse events associated with these hand sanitizer products. FDA encourages health care professionals, consumers and patients to report adverse events or quality problems experienced with the use of hand sanitizers to FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program:
Source: US Food and Drug Administration July 2020
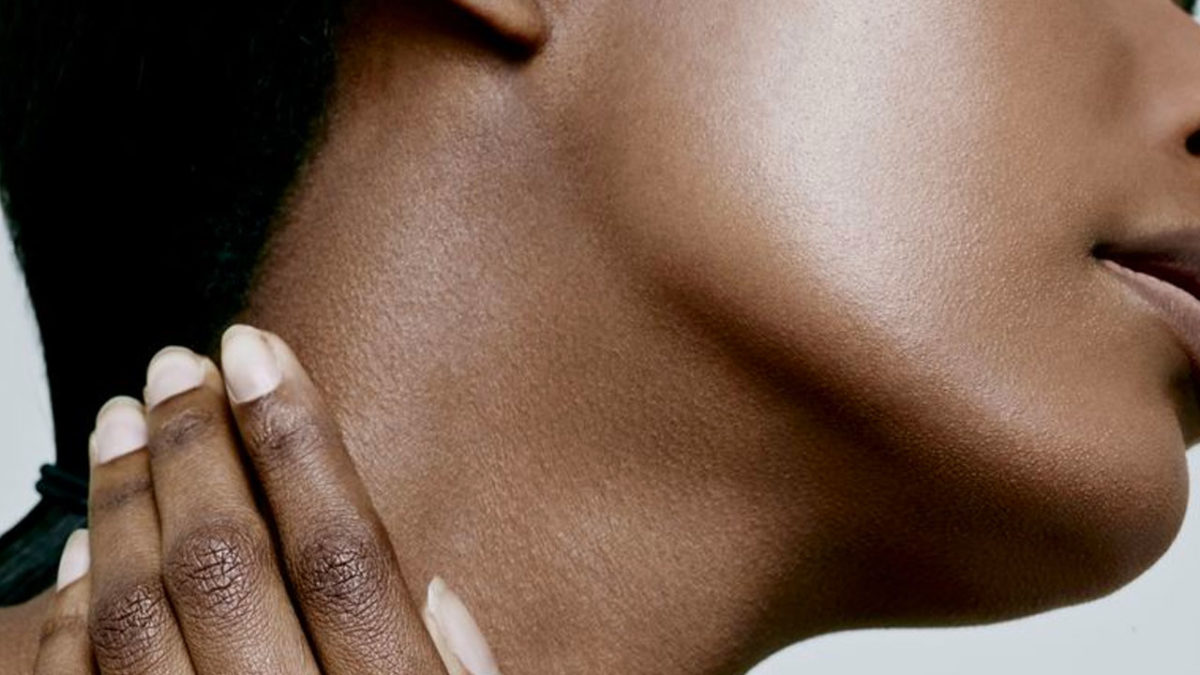
Good skin care involves more than just your face. Many users of washes, moisturizers and skin rejuvenation products apply them only to the visible regions of the face. Have you forgotten to take care of your neck while focusing on your face? Here are a few things which may help…..
Nourish Your Neck
Have you noticed that your skin is starting to look a bit dull? When the harsh summer sun gives way to the dryness of indoor heat, your skin may also turn dry and dull. Smooth your moisturizer and/or hydrator down past the collarbone area to keep both neck and décolleté soft and firm.
Protect It
Apply sunscreen every day! We recommend sunscreens that contain zinc oxide >6% which protects you from burns, skin cancers, and premature aging. Even while indoors or driving, you are exposed to UV (under fluorescent lighting, through windows, etc.) Over the years, sun exposure/burn can lead to dark spots, wrinkles, and skin laxity. Apply to face, neck, and décolleté. Physician-grade sunscreens include the following: Elta MD has several formulations of sunscreen with zinc oxide >9%; Eraclea 4 in 1 has 20.5% zinc oxide; ISDN Eryfotona has 11% zinc oxide and is formulated not only to protect but also to repair sun damage.
Moisturizers
Over the counter moisturizers for the neck include Cerave Moisturizing Cream, Cetaphil Restoraderm, and Neutrogena Hydro Boost. Physician-grade moisturizers (from physicians’ offices and not over-the-counter) include Sorbolene, Avene Xeracalm Balm, Sente Dermal Repair (see below), Skinbetter Face and Neck Cream, and Skin Better Trio.
Sente Dermal Repair Cream is another great moisturizing option. This product contains Heparan Sulfate Analog (in the same family as injectable hyaluronic acid fillers), a revolutionary repairing molecule that helps reduce redness, delivers deep hydration, and support the skin’s ability to repair itself. In a clinical study, 100% of subjects had increased skin hydration starting from week 2 through study completion at week 8. 73% of subjects showed improvements in fine lines and wrinkles at week 8.
Hydrators
How are moisturization and hydration different? Simply put, hydration equals water, and moisture equals oil. If your skin is dehydrated, it is lacking water. To hydrate your skin, drinking plenty of water is key. Reminder that drinking caffeine dehydrates. Topical hydration products that are physician-grade include Eraclea Hydration Serum.
Firm Up
Apply products specifically made for the neck. They can nourish as well as regenerate. Physician-grade products include Sente Neck Firming Cream, which is formulated with patented Heparan Sulfate Analog (HSA) technology ((in the same family as injectable hyaluronic acid fillers) to rapidly and profoundly hydrate and strengthen the skin’s natural ability to repair itself. This cream improves the appearance of crepey skin and horizontal neck lines. It also contains caffeine, an ingredient known to help tighten and brighten the skin.
Get Even
For fading dark spots, use a physician-grade brightener such as Eraclea Reveal (containing Nicinamide PC, Synovea® HR a safe and effective hexylresorcinol that is used as a skin lightener and is clinically proven to be four-times more effective than Hydroquinone. Licorice Extract – used for its antioxidant and lightening properties. Kojic Acid is used as a skin toner and lightener.) or SkinBetter Even Tone. Even Tone, featuring the patented a ground-breaking, non-hydroquinone, non-retinol formula that delivers a visibly dramatic reduction in the appearance of hyperpigmentation.
Smooth Those Lines
Retrinals and Retin-A are the best to smooth wrinkles. Apply in the evening to help exfoliate and stimulate collagen. Consider a physician grade skin smoothing cream like SkinBetter AlphaRet. AlphaRet is the latest innovation in retinoid renewal delivering remarkable results, with little-to-no irritation compared to other retinoids and retinoid-based products.
Posture
Be aware of your posture as you read your smart phone or work at the computer. Constantly bending your head down can exaggerate wrinkles. Try sleeping on your back so you don’t press wrinkles into your cheeks or chest.
FOR ADVANCED NECK CARE….
Pelleve radio-frequcncy treatments can firm and tighten the skin. This is an in-office procedure with very minimal downtime. See before and after pics here
Kybella treatments can permanently remove fat and produce secondary tightening of skin. This is an in-office injection performed by Dr Moore.
For more information, simply ask your Provider at your next office visit or call Pat at 817-795-7546 ext 304 or orders@acderm.com